La importancia del entorno cultural
Las normas y valores sociales, culturales y religiosos de un país tienen un impacto muy significativo en el sistema de decisiones del mix de marketing. Además de afectar y definir las relaciones entre comprador y vendedor, estas variables culturales influyen directamente en las preferencias y comportamientos de compra de los consumidores y por tanto afectan directamente a las políticas de producto y comunicación.
Diferencias culturales como carne de vaca en la india o cerveza sin alcohol en los países musulmanes.
En el entorno cultural en el marketing internacional, obtener información sobre las características culturales es habitualmente más difícil que obtener información del sistema económico. Pero el éxito de un programa de marketing dependerá en su mayoría de la sensibilidad a estas variables culturales. Las culturas condicionan los hábitos y los comportamientos de los consumidores. Dentro de la cultura podemos encontrar los gustos, los valores, las actitudes, la religión, la estética entre otros.
Los especialistas en marketing internacional deben ser conscientes de cómo la cultura influye en los gustos y formas de consumo y cuáles son los principales factores, cambios y tendencias culturales en sus respectivos mercados.
Edward Taylor define la cultura como: “El conjunto complejo de conocimientos, creencias, arte, moral , leyes, costumbres, y cualquier otra capacidad o hábito adquirido y aprendido por un individuo como miembro de una sociedad”.
Elementos del entorno cultural en los negocios internacionales
Religión: Objetos sagrados, sistemas filosóficos, normas, creencias, tabúes, vacaciones, rituales y rezos.
Lenguaje: Hablado, escrito, idiomas oficiales, pluralismo lingüístico, jerarquía del lenguaje, medios de comunicación.
Valores y atributos: Orientación formal, formación profesional, educación primaria, educación secundaria, universitaria o nivel de alfabetización.
Ley: Ley común, derechos humanos, leyes internacionales, ley del país de origen, leyes anti competencia (antitrust) y otras regulaciones legales.
Política: Racionalismo, soberanía, imperialismo, poder, intereses racionales, ideologías, riesgo político.
Organizaciones sociales: instituciones sociales, estructuras de autoridad, grupos de interés, movilidad social, estratos sociales, sistema social.
Tecnología y cultura material: Transporte, energía, sistemas, instrumentos y mecanismos, comunicación, urbanización e investigación científica.
En el entorno cultural en los negocios internacionales, analizar todos estos valores a la hora de tomar decisiones de marketing no es nada fácil, por suerte existen diversos modelos analíticos que nos permiten valorar cómo las distintas variables culturales afectan de forma directa o indirecta a las respectivas decisiones empresariales y formas de hacer negocios a nivel internacional.
Algunos de ellos analizan los elementos importantes del entorno cultural y cómo éste afecta a las distintas variables del marketing mix.
Otros modelos tienen una perspectiva antropológica de la cultura. Un ejemplo claro de este tipo de modelos puede ser el de las dimensiones culturales de de Hofstede.

Elementos culturales y su impacto en el marketing internacional
Antes de realizar un plan de marketing internacional para una determinada región, es importante analizar la forma en la que los consumidores perciben y utilizan los productos o servicios. También estudiar sus valores, creencias, prejuicios y demás elementos que puedan estar afectando a la forma de negociación con nuestros clientes o proveedores, o a la forma de posicionar y comunicar nuestro producto en el mercado.
1. Costumbres de consumo
¿Cómo la sociedad gasta dinero en las distintas categorías de productos y servicios? Distintas distribuciones de gastos según culturas. Se consumen más algunas categorías de producto que otras.
Otros aspectos a considerar serán aquellos relativos a la percepción de la riqueza y la proyección social del estatus y prestigio social. Culturas como la estadounidense exteriorizan fácilmente el éxito social y la riqueza. Exteriorizar la riqueza como algo positivo, lo cual dista mucho de la visión que tenemos en España del rico.
2. Instituciones sociales e interacción social
Dentro de los valores culturales, debemos diferenciar los primarios de los secundarios. Los primarios son los más persistentes, las creencias y valores fundamentales que se transmiten de padres a hijos y son reforzados por las instituciones sociales más importantes: Escuelas, empresas, familia, gobierno, iglesia, etc. Las creencias y valores secundarios están más expuestos al cambio. Creer en el matrimonio se trata de una creencia primaria, mientras que creer en que las personas deben casarse pronto es una creencia secundaria. En términos generales, es mucho más fácil actuar sobre los valores secundarios que sobre los primarios.
La variable de interacción social se centra en las relaciones sociales respecto al género (hombre vs mujer), la concepción de la familia, el valor de la edad, las relaciones de poder entre jefes y subordinados, etc. La familia es la institución básica por excelencia en la mayoría de las sociedades. Pero, esta puede tener significados distintos en los distintos países. Este tipo de variables afectan también a los procesos de negociación y relaciones personales. En muchas culturas, la edad es un símbolo de experiencia y respeto.
3. Comunicación y lenguaje
El idioma y las lenguas son un aspecto crítico en el entorno cultural, el idioma es la diferencia más obvia entre culturas. Esto en muchas ocasiones se trata de una oportunidad, en otras ocasiones es una gran amenaza. En muchos países se habla más de una lengua y diversos dialectos. Cuando una empresa entra a comercializar en un país como Estados Unidos en el cual los 330 millones de habitantes hablan inglés, lo hace en un único idioma, mientras que si entra a hacerlo en algún país europeo, tendrá que hacerlo en varios idiomas y para una población mucho menor.
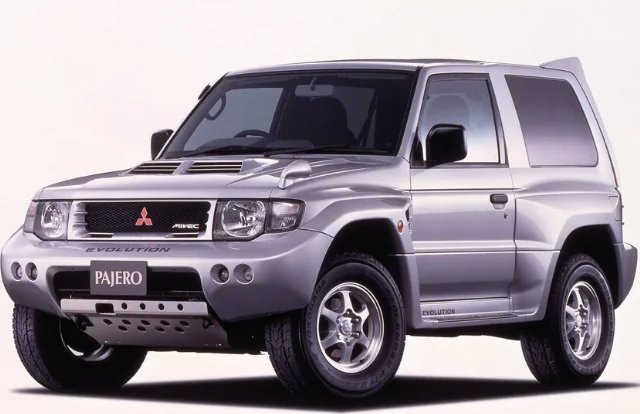
Las distintas lenguas e idiomas afectan directamente a las políticas de marca, eslogan, publicidad, entre otros. También son comunes los problemas a la hora de transferir el nombre de marca, pudiendo en un país tener connotaciones negativas y en otro positivas, debido que ambas tienen un contexto cultural distinto. Este puede ser el caso del Mitsubishi Montero, que en sus orígenes fue llamado Mitsubishi Pajero, obteniendo su nombre de un felino (Leopardus Pajeros). El nombre de este coche tuvo que cambiar en los países hispanohablantes, pero esto no ocurrió hasta la tercera generación. Lo mismo ocurrió con el Mazda Laputa o bien con el Nissan Moco.
Escoger un buen nombre de marca o bien de productos influye enormemente en la imagen percibida por el consumidor incluso de la calidad de la empresa y del producto. En los países asiáticos, es habitual que exista monopolio o duopolio en muchos mercados de consumo, se le asigna una importancia incluso mayor que en occidente a las marcas y su imagen. Esto es debido a la gran lealtad, el cual se atribuye a ciertos valores culturales asentados en países como China como la distancia al poder, aversión al riesgo y orientación colectivista y de conformidad con las normas del grupo de referencia.

De la misma manera, hay que ser igual de meticulosos con los logotipos y eslóganes. Los eslóganes en raras ocasiones al ser traducidos literalmente conservan su significado. Cada vez es más popular establecer un eslogan en inglés exportable al ámbito internacional. De igual manera, el idioma no sólo influye en la comunicación con el consumidor, estas dificultades también se encuentran en las corporaciones internacionalizadas internamente y con los proveedores y clientes mayoristas. Los directivos de las distintas sucursales en distintos países hablan diferentes idiomas y tienen culturas distintas. Por ello es importante informarse previamente sobre normas de protocolo y negociación. Esto influye por ejemplo en los tiempos de decisión, en oriente, estos son mucho más largos que en occidente, mientras que en Estados Unidos, consideran que el tiempo que se tarda en decidir es dinero perdido y en los países árabes y latinos, se prefiere establecer una relación antes de confiar en la otra empresa o persona.
4. Religión
La religión es sin duda uno de los elementos más importantes en el entorno cultural de una sociedad. Llegando a representar una gran oportunidad y en ocasiones una absoluta imposibilidad de comercialización de un producto.
De igual manera las creencias religiosas afectan directamente a los valores, normas, creencias y comportamientos de consumo de las distintas sociedades. Los casos más claros pueden ser la necesidad del certificado Kosher para los judíos o bien el certificado Halal para los musulmanes. Estando muy limitado la comercialización del cerdo o del alcohol en países musulmanes. Por el contrario, si sabemos distinguir las necesidades de los religiosos y amoldar nuestro producto a ellos, podemos encontrar una gran oportunidad de negocio. Por otro lado, las negociaciones pueden verse afectadas por la cultura y religión de las partes negociantes, como en aquellas culturas en las cuales se necesita el consentimiento de la institución religiosa o del Dios al que adulan.
5. Estética y colores de los productos
La estética juega un papel importante en la comercialización de los productos. Es un término subjetivo que viene condicionado por el entorno cultural del país. Un claro ejemplo es el de Arabia Saudí, que usa sólo maniquíes sin cabeza ni brazos, de igual manera las Barbies en los países árabes se modifican estéticamente para que cumplan los cánones de vestimenta y de belleza. Los colores también juegan un papel muy importante, en muchas ocasiones un color se asocia directamente en un determinado país con una categoría de producto. Por poner un ejemplo, mientras que en occidente el blanco representa una imagen de fuerza física y pureza, en ciertos países de Asia se asocia a la muerte y al luto.
Otros condicionantes culturales
Ética y moral
Otra variable a tener en cuenta es la tendencia social sobre los aspectos éticos, humanitarios, sociales o medioambientales. Estos aspectos pueden no sólo castigar o premiar los actos de las empresas productoras y distribuidoras, si no a todas las empresas originales de un cierto país u origen.
Orgullo y prejuicios
los prejuicios, las supersticiones, el orgullo nacional y el etnocentrismo entran dentro de de esta categoría. Las símbolos nacionales, animales protegidos, números de la suerte, bromas típicas y sentimientos nacionales deben ser tenidos en cuenta. De manera que en ocasiones, aquellas marcas que se posicionan son aquellas que son capaces de adquirir determinada cuota de mercado, muchas veces abrazando los estereotipos o tópicos como puede ser la Mecca-Cola en los países árabes, Inca-Cola en Perú o bien Cola-Turka en Cuba.
De igual manera, el país productor de los productos vendidos en otro, tiene per se una imagen determinada en él. Lo que puede ocurrir con España con los coches producidos en Alemania o bien las motos producidas en Japón. Existe un paraguas que hace esos determinados productos más o menos fiables.
Modelo de dimensiones culturales de Hofstede
Se trata del modelo más popular para clasificar los países, nos ayuda a valorar e identificar los comportamientos culturales de cada región o grupo cultural. Así, podemos comprender mejor otras culturas, examinando los valores culturales que pueden afectar a su comportamiento, decisión y pensamiento. En este artículo te explicamos en detalle las 6 dimensiones culturales por las cuales segmenta las culturas.
LAS 6 DIMENSIONES CULTURALES DE HOFSTEDE
Distancia al poder: se ocupa de la actitud de la cultura hacia las desigualdades entre los individuos.
Individualismo: Analiza el grado de interdependencia que mantiene una sociedad con sus miembros.
Masculinidad: Marca que la motivación surge a través de la competencia, los logros y el éxito.
Control de la incertidumbre: Trata la forma en la que una sociedad lidia con el hecho de que el futuro es desconocido.
Orientación a largo plazo: Describe cómo las sociedades ordenan sus prioridades entre sus vínculos pasados y los desafíos presentes y futuros.
Indulgencia: Se refiere al grado en el que las personas que constituyen una sociedad tratan de controlar sus impulsos y deseos.
Cerviño, J., (2013). Merketing Internacional; Nuevas perspectivas para un mercado globalizado, Madrid, España: Pirámide.
¿Quieres desarrollar un estudio de mercado para conocer mejor las regiones en las que operar, o bien necesitas un plan de marketing? en Klawter te ayudamos con lo que necesitas con estudios hechos a tu medida. ¡Contáctanos y háblanos de tu caso!